-Rajneesh Saroj, GM (Civil)/NHSRCL
Synopsys
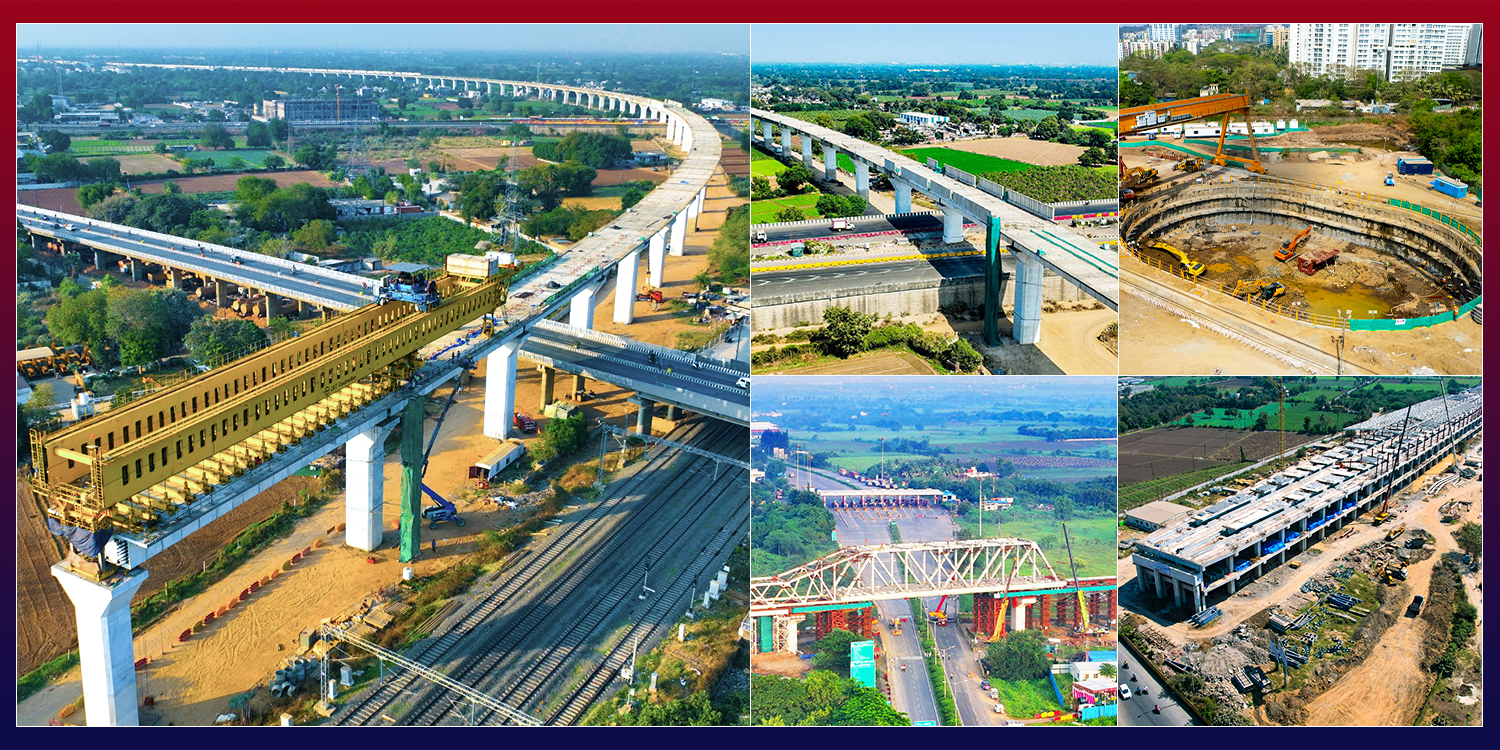
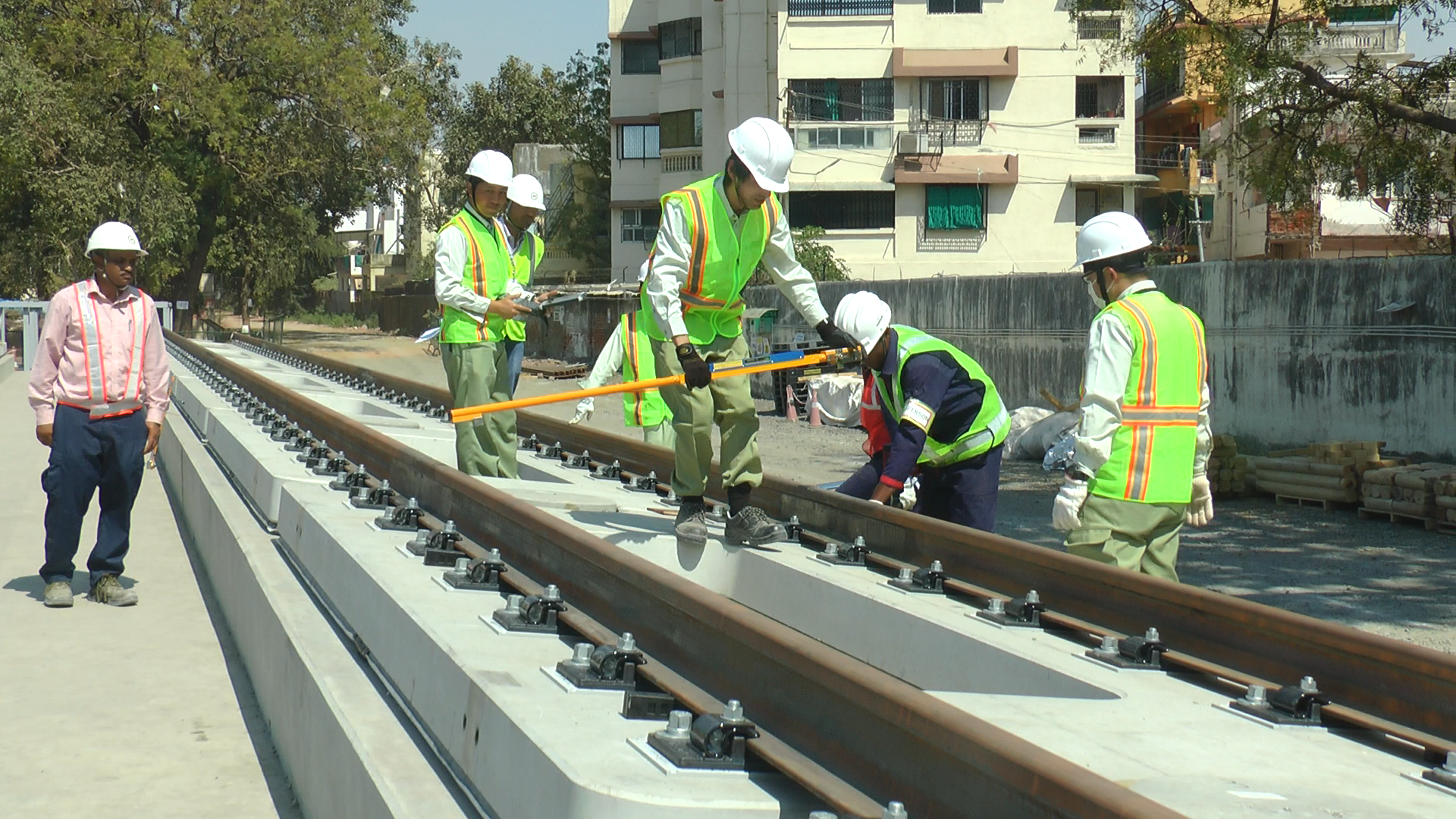
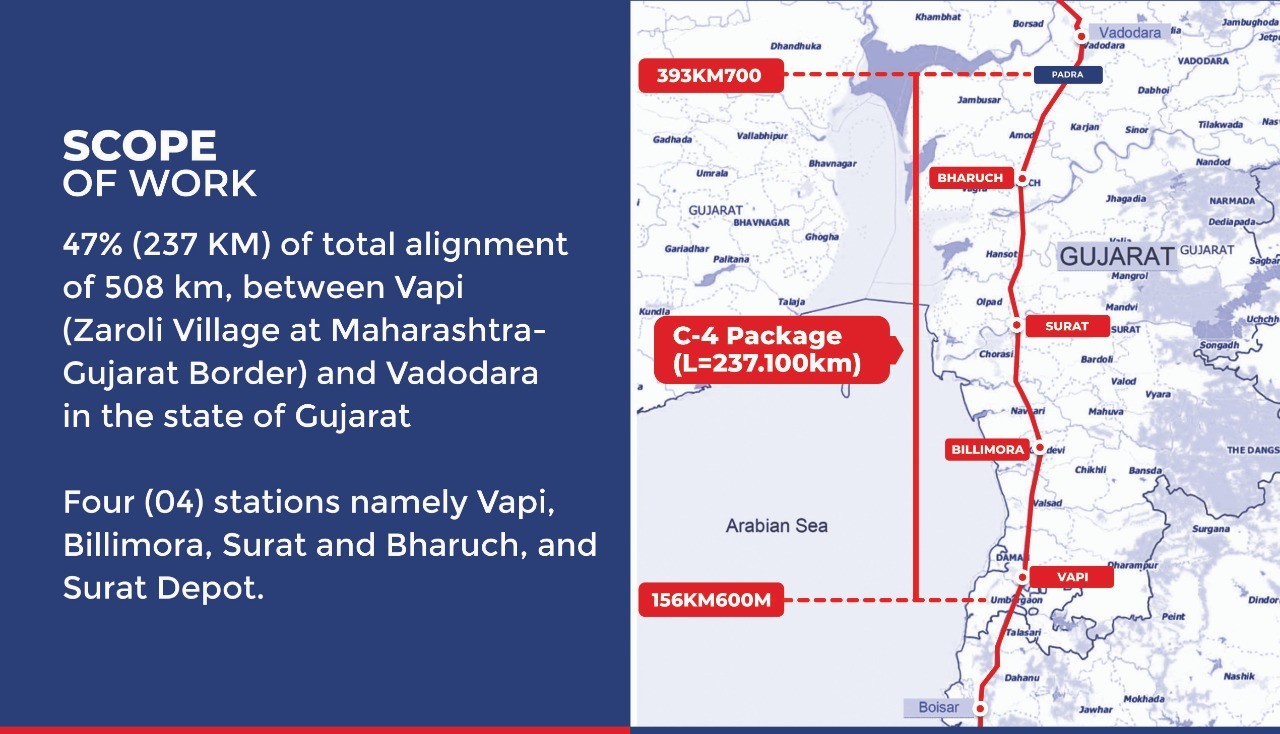
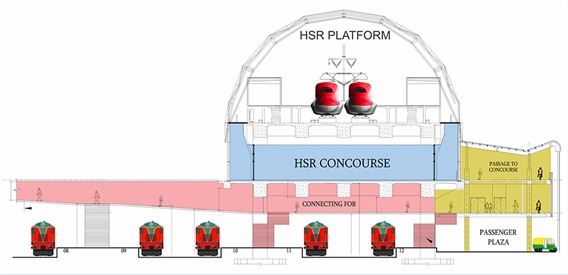
This technical paper delves into a comparative analysis of steel bridge fabrication methods employed in Japan and traditional practices in India, with a specific focus on the Mumbai Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail (MAHSR) project's adaptation of Japanese techniques. Japan's cutting-edge approach to steel bridge construction, characterized by mechanization, precision, and stringent quality control, is examined in contrast to the conventional methods utilized in India.…